What is cellular nutrition? It’s a revolutionary way of looking at health. Instead of focusing on organs—like the heart or liver—it focuses on the trillions of individual cells that build those organs. Because you are only as healthy as your cells.
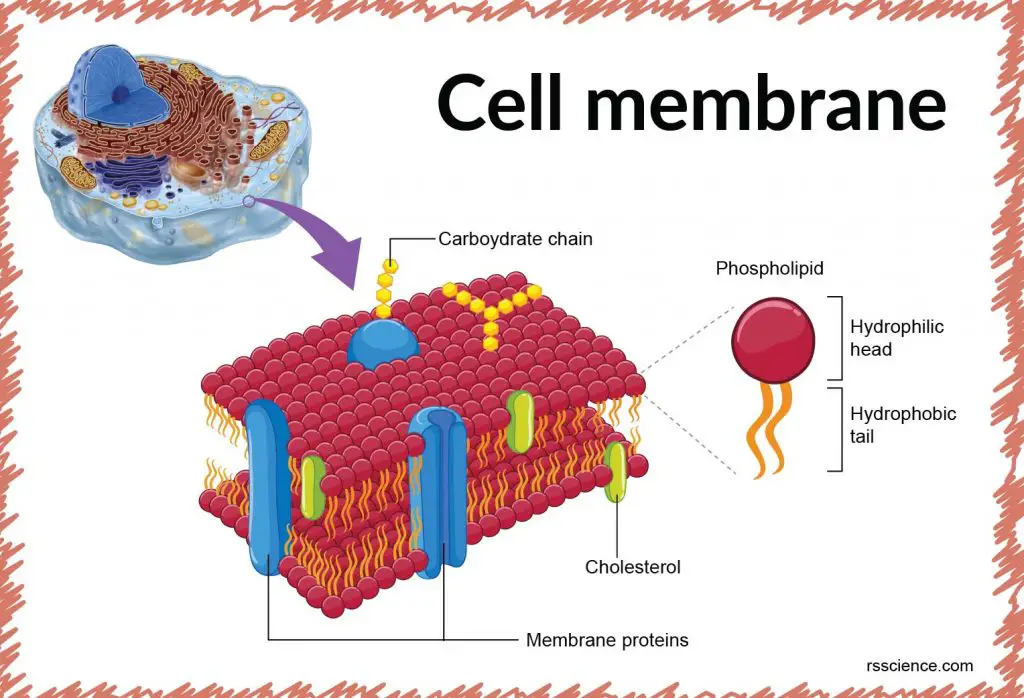
The answer lies in the cell membrane. And the key to a healthy membrane is found in the “good fats”—the lipids and sterols—that modern food processing has systematically stripped from our diet1.
This post explores the revolutionary science of your cell membrane, the clinical proof that feeding your cells works, and how this impacts your energy, health, and vitality.
🔬 What is Cellular Nutrition? The “Starved” Cell Analogy
For decades, modern food processing has “refined” our grains—like wheat, rice, and soy—to create staples like white flour and white rice. This process strips away the nutritious outer layers to increase shelf life, but in doing so, it removes the most vital nutrients: the lipids and sterols2.
This has created a critical deficiency in our diet, and it has a direct effect on our cells.
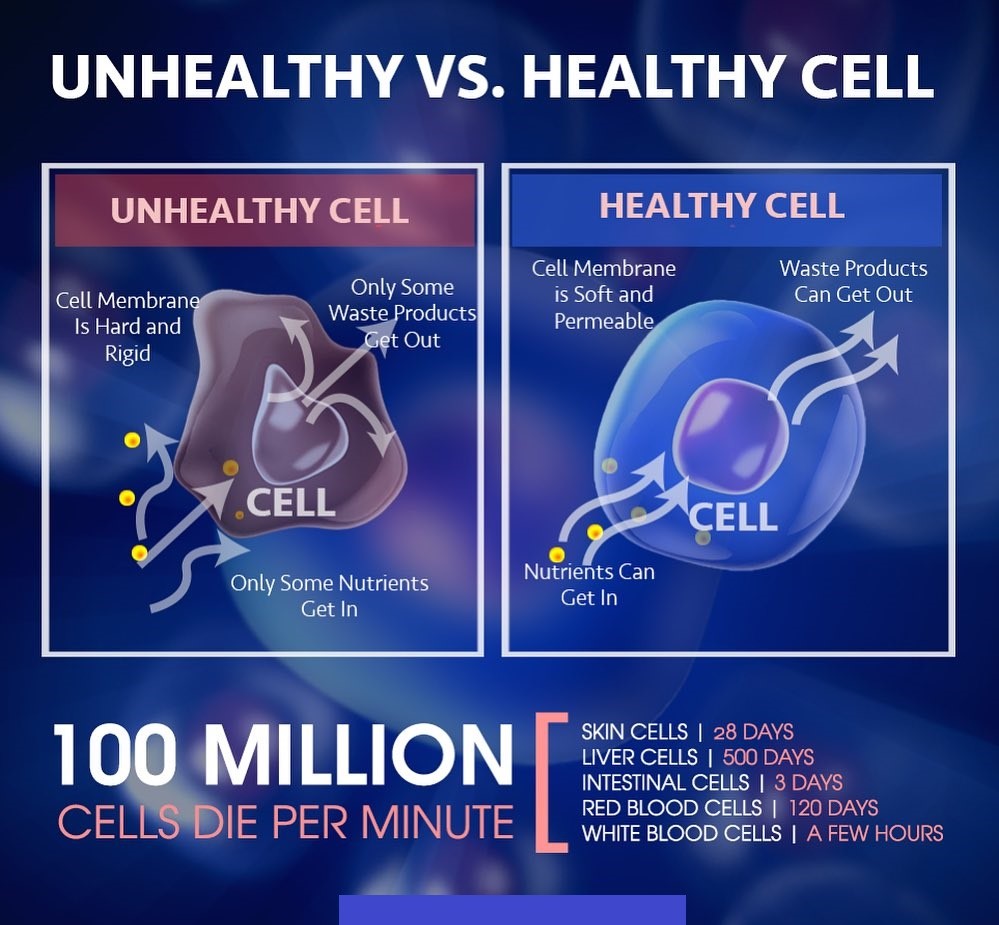
Here’s why: Every single one of your trillions of cells is surrounded by a membrane. This membrane is the “gatekeeper,” and it’s built from the fats (lipids and sterols) you eat3. A healthy membrane is “pliable” and flexible, with the discretionary power to:
- Allow nutrients IN.
- Allow waste and metabolic products OUT4.
When our diet is deficient in these critical lipids and sterols, our body must build cell membranes from the wrong materials (like processed or artificial fats). These membranes become rigid and dysfunctional.
This leads to a state of cellular inefficiency. The cells become:
- “Starved”: They are inhibited in their ability to absorb nutrients, even when they are available.
- “Constipated”: They are inhibited in their ability to eliminate accumulating waste products.
Under these conditions, your cells work inefficiently, expending far more energy than healthy cells would to get the same results. This concept isn’t new. In the 1950s, Southern California doctors investigating “chronic fatigue” drew a direct connection between reduced cellular energy and the absence of these whole-grain dietary lipids.
💡 The Insight: Why the Cell Membrane is the “Boss”
This “starved and constipated” state isn’t just an analogy; it’s the root of metabolic dysregulation.
We used to think of the nucleus (DNA) as the “brain” of the cell. But cutting-edge science reveals that the cell membrane is the true “boss.” A 2016 review in the American Journal of Physiology called the plasma membrane the “primary and critical regulator of stress and disease adaptation of the cell”.
It’s not just a wall; it’s an intelligent “capacitor for energy and metabolism”11.
The fats you eat directly build this “boss” And a poorly built membrane is now scientifically linked to major chronic diseases:
- Metabolic Syndrome: A dysfunctional membrane, built from the wrong dietary fats, is directly associated with the cluster of diseases known as the metabolic syndrome.
- Type 2 Diabetes: This link is measurable. A 2014 study in the American Journal of Clinical Nutrition analyzed the membranes of red blood cells. It found that specific fatty acid compositions were longitudinally associated with changes in glycemia and the risk of developing type 2 diabetes. A 2022 study confirmed this, finding that low percentages of key vegetable fats in cell membranes were associated with worse glucose metabolism.
💡 The Insight: The Membrane-Mitochondria Energy Connection
This is the second critical piece of the puzzle. The health of your cell membrane (the “boss”) directly controls the function of your mitochondria (the “power plant”).
A 2019 study published in PLoS One looked at the effects of Rice Bran Oil (RBO)—a key whole-food lipid and sterol concentrate. The study made a groundbreaking discovery: RBO directly enhances mitochondrial respiration.
In simple terms, it helps your mitochondria work better. The RBO treatment was shown to upregulate basal respiration, maximal respiration, and, most importantly, ATP production.
And what is the result of this increased mitochondrial energy? The study concluded that this enhancement is the mechanism by which RBO ameliorates (soothes) inflammatory responses.
Healthy Lipids ➡️ Healthy, Pliable Membranes ➡️ Efficient Mitochondria ➡️ More ATP (Energy) ➡️ Less Inflammation
🧬 The Proof: The Texas A&M University Study

This all makes scientific sense, but is there direct proof that supplementing with these lipids and sterols actually works?
Yes.
A compelling study was conducted at Texas A&M University to measure the precise effects of Tre-en-en Grain Concentrates. The study compared a control group to a test group that had Tre-en-en added to their diet.
The results were dramatic and provided the first major proof of cellular nutrition:
- Improved Nutrient Utilization Efficiency: The group with Tre-en-en showed significantly higher efficiency in how their bodies utilized nutrients for growth and development. This is the clinical proof that Tre-en-en solves the “starved cell” problem.
- Superior Cardiovascular Development: The Tre-en-en group showed measurably greater cardiovascular development.
- Enhanced Overall Growth & Development: The test group demonstrated significantly greater overall growth and development, proving that with their cells finally “fed,” their bodies could function at a higher level.
This study is further supported by a mountain of research on whole grains. The 1999 Nurse’s Health Study (75,000 nurses) showed whole-grain consumption lowered the risk of heart disease by 25% and stroke by 36%. A 2000 JAMA study showed a nearly 50% reduction in ischemic stroke risk for people who consumed whole grains.
🧬 The Solution: The Original Answer to “What is Cellular Nutrition?”

Based on the original “chronic fatigue” research in the 1950s, NeoLife’s Scientific Advisory Board (SAB) created Tre-en-en® Grain Concentrates in 1958. It was, and still is, the world’s first phytonutrient supplement.
Named for the Greek “3-in-1,” Tre-en-en is not a multivitamin. It is a unique, exclusive blend of concentrated lipids and sterols from whole wheat germ, rice bran, and soybeans.
It was designed to solve one problem: to feed your cells.
It provides the complete spectrum of phyto-LIPIDS (including omega-6s and omega-3s) and phyto-STEROLS (like beta-sitosterol, gamma-oryzanol, and stimasterol) that your body needs to build healthy, “pliable” membranes.
By fixing the “good fat” deficiency caused by food processing, Tre-en-en helps ensure nutrients get in and waste gets out, promoting the efficient functioning of your cells and strengthening the “link” in your “Chain of Life”.
🩺 Science Over Shelf Hype
Stop trusting $20 shelf supplements that hide behind flashy claims. The market is flooded with fakes, fillers, and contaminants.
Choose traceable, science-backed cellular nutrition — proven in human trials. NeoLife’s solution is built on whole-food ingredients, guaranteed for purity, and backed by a world-class Scientific Advisory Board since 1958.
This is not a “pill”—it’s an investment in your cellular health.
👉 Explore NeoLife’s Cellular Nutrition Range — anchored by the original Tre-en-en® — where purity meets performance.
🔗 Also read:
- The Ultimate Guide to Mitochondrial Health: Your Cellular Powerhouses Explained.
- From “Insurance” to “Investment”: The New Science of Multivitamins and Memory.
References
- Ray S, Kassan A, Busija AR, Rangamani P, Patel HH. The plasma membrane as a capacitor for energy and metabolism. Am J Physiol Cell Physiol. 2016;310(3):C181-C192.
- Hulbert AJ, Turner N, Storlien LH, Else PL. Dietary fats and membrane function: implications for metabolism and disease. Biol Rev Camb Philos Soc. 2005;80(1):155-169.
- Mahendran Y, Ågren J, Uusitupa M, et al. Association of erythrocyte membrane fatty acids with changes in glycemia and risk of type 2 diabetes. Am J Clin Nutr. 2014;99(1):79-85.
- Chiva-Blanch G, Giró O, Cofán M, et al. Low Percentage of Vegetable Fat in Red Blood Cells Is Associated with Worse Glucose Metabolism and Incidence of Type 2 Diabetes. Nutrients. 2022;14(7):1368.
- Marklund M, Wu JHY, Imamura F, et al. Biomarkers of Dietary Omega-6 Fatty Acids and Incident Cardiovascular Disease and Mortality. Circulation. 2019;139(21):2422-2436.
- Lee S, Yu S, Park HJ, Jung J, Go GW, Kim W. Rice bran oil ameliorates inflammatory responses by enhancing mitochondrial respiration in murine macrophages. PLoS One. 2019;14(10):e0222857.

Pingback: What Are Flavonoids and Polyphenols? The Science of Antioxidants
Pingback: Coenzyme Q10: A Complete Guide to the Science and Benefits